First-party data integration combines data from different sources to facilitate richer analytics and drive smarter business decisions. This involves a person or system locating, retrieving, cleaning, and presenting the data.
The query runs against the merged data and helps unlock business intelligence. Businesses need to take the time to align their goals with the right approach.
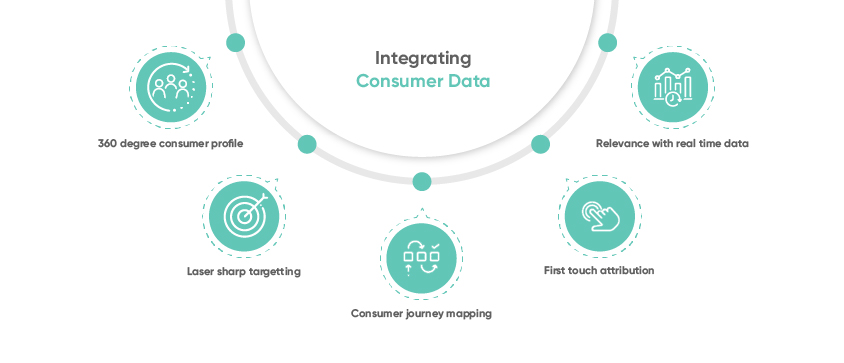
Data integration helps drive unique advantages for marketers. A few key benefits are highlighted below:
Create a 360-degree view of the consumer
Multiple identities or anonymous profiles represent each consumer as they engage with a brand offline and online touchpoints. Merging these profiles to have a single view helps get a comprehensive understanding of the consumers and their actions across various channels, devices, and platforms.
Improve targeting precision
To improve audience addressability and target efficiently, marketers need to migrate from cookie-based targeting to the brand’s first-party data strategy to unify consumer identities with real people across devices and channels. Audience unification enhances higher accuracy and relevancy, reduces ad waste, and ultimately improves ROI.
Map the customer journey
Accessing first-party consumer data from across sources and integrating them into one consumer identity asset can provide the holistic buying journey of the consumers, discovering the different consumer steps on their path to conversion along with the order in which they take various actions. This, in turn, helps marketers deploy the right message at the right time and place, deploying a strategy to pull customers back on the path to conversion.
Close the loop on attribution
Insights from integrating first-party data from various sources and touchpoints are employed to influence media allocations and budgets. Exploring how each event in the consumer journey affects conversion and how each touch point contributes to the conversion provides more accurate attribution guidelines to improve online engagement to in-store sales through investment reallocation.
Improve relevance
First-party data integration, with the most precise consumer intelligence, helps the brand to innovate ways to tailor messaging to shape the most sought-after consumer experiences. Based on the rich insights emerging from the data integration related to consumer behaviors across touchpoints, unique brand experiences are customized to specific interests, preferences, locations, and purchase histories.
It’s essential to understand the five types or techniques of first-party data integration with their respective pros and cons to grasp the subject better.
Manual data integration
Manual data integration is a technique where all integration aspects are managed manually by connecting different data sources and collecting and cleaning the data without automation.
Pros:
- Reduced cost: This technique requires little maintenance and can only integrate limited data sources.
- Greater freedom: The user has total control over the integration.
Cons:
- Less access: Only manual orchestration of each integration by the manager
- Difficulty scaling: Scaling up is impossible and time-consuming by manually changing the code for each integration
- Greater room for error: Data must be handled and controlled at each stage.
This strategy is best suited for one-time instances but untenable for complex or recurring integrations due to its manual process that might consume unproductive time and resources.
Middleware data integration
Middleware (software) connects applications and transfers data between them and databases. It’s especially handy when a business is integrating stubborn legacy systems with newer ones, as middleware can act as an interpreter between these systems.
Pros:
- Better data streaming: The software conducts the integration automatically and in the same way each time.
- Easier access between systems: The software is coded to facilitate communication between the systems in a network.
Cons:
- Less access: The middleware needs to be deployed and maintained by a technically sound developer
- Limited functionality: Middleware can only work with certain systems
Middleware is ideal for businesses integrating legacy systems with more modern systems, middleware is ideal, but it’s mostly a communications tool and has limited data analytics capabilities.
Application-based integration
Here software applications do the locating, retrieving, cleaning, and integration of data from disparate sources. This compatibility helps the easy transfer of data from one source to another.
Pros:
- Simplified processes: Single application-based operation
- Smooth information exchange: Enables systems and departments to transfer data seamlessly.
- Fewer resources requirement: Due to the automated process, minimal human intervention needed
Cons:
- Limited access: Requires specialized technical knowledge to access and maintain the process
- Inconsistent results: No standardized for all setups, and thus, results vary by set-up
- Complicated setup: Complicated designing for it to work seamlessly across departments and thus challenging to maneuver
- Complex data management: Accessing different systems can lead to compromised data integrity
This system works better for enterprises operating in hybrid cloud environments where they work with multiple data sources — on-premises and in the cloud. This approach optimizes data and workflows between these environments.
Common storage integration
A similar approach to uniform access involves creating and storing a copy of the data in a data warehouse. Thus, it is more versatile in how businesses can manipulate data; therefore, it has become one of the most data integration forms.
Pros::
- Reduced burden: The host system isn’t constantly handling data queries.
- Increased data version management control: Accessing data from one source versus multiple disparate sources leads to better data integrity
- Cleaner data appearance: The stored copy of data allows numerous query runs while maintaining data appearance uniformity
- Enhanced data analytics: Stored copy allows time and scope for running more sophisticated queries
Cons:
- Increased storage costs: Creating data copy leads to more storage cost
- Higher maintenance costs: integration requires higher technical expertise for maintenance and supervision
It is the most sophisticated and sought-after integration approach supported with the right resources and provides deeper consumer insights.
Inability to build a Coherent Data Integration Strategy:
This essentially means knowing the sources, the types, and the processes of first-party data collection and mapping it across the customer journey based on the relevance to the brands. Many companies face huge challenges in formulating such a strategy and thus compromise on the benefits of data integration.
Bottlenecks in instituting the data integration process:
Integration requires the enterprises to have specific tools to assimilate the customer engagement data in the fragmented silos within the organization, with the third-party technology partners, and across various other channels. Such tools help to facilitate the necessary integration in providing a big picture of the consumer data to shape holistic customer profiles.
Shortcomings in building a unified consumer profile:
As consumers engage with a brand across various channels, the customer data exists in multiple profiles and ids across various disjointed platforms which need to be merged In order to unlock a unified view of each customer. Only this can ensure the building of a customized, dynamic connection strategy that drives better consumer responses without wasting marketing dollars or overwhelming them.
Indifference to data redundancy and real-time action needs
The value and relevance of data decay quickly. This is aggravated by the rapid and constant changes in consumer preferences and behaviors. It is imperative that an enterprise, along with its first-party data partner, must prioritize the value of data recency and the need for its real-time action to make them available to the relevant internal and external stakeholders to take a ride on the acquired consumer knowledge before it gets irrelevant. After acquiring consumer data, companies often keep reactivating them beyond the stipulated data validity period and thus create communication programs that don’t resonate with the consumers.
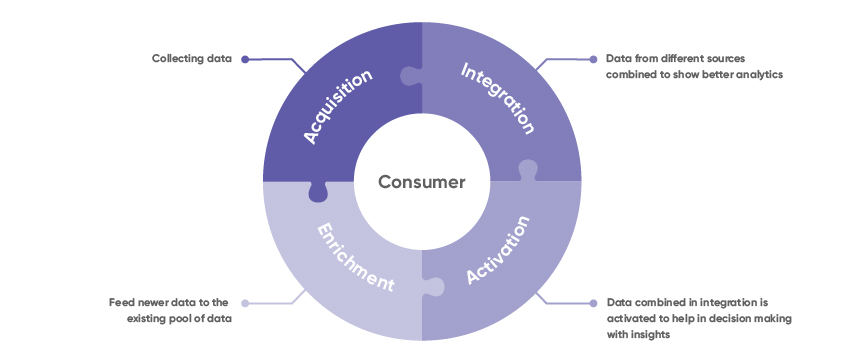
Grivy provides a seamless, holistic single-window solution for first-party data acquisition, enrichment, activation, and required integration on one platform backed up by advanced technology support and working closely with the brand and data team to drive the best-in-class system and business results.











